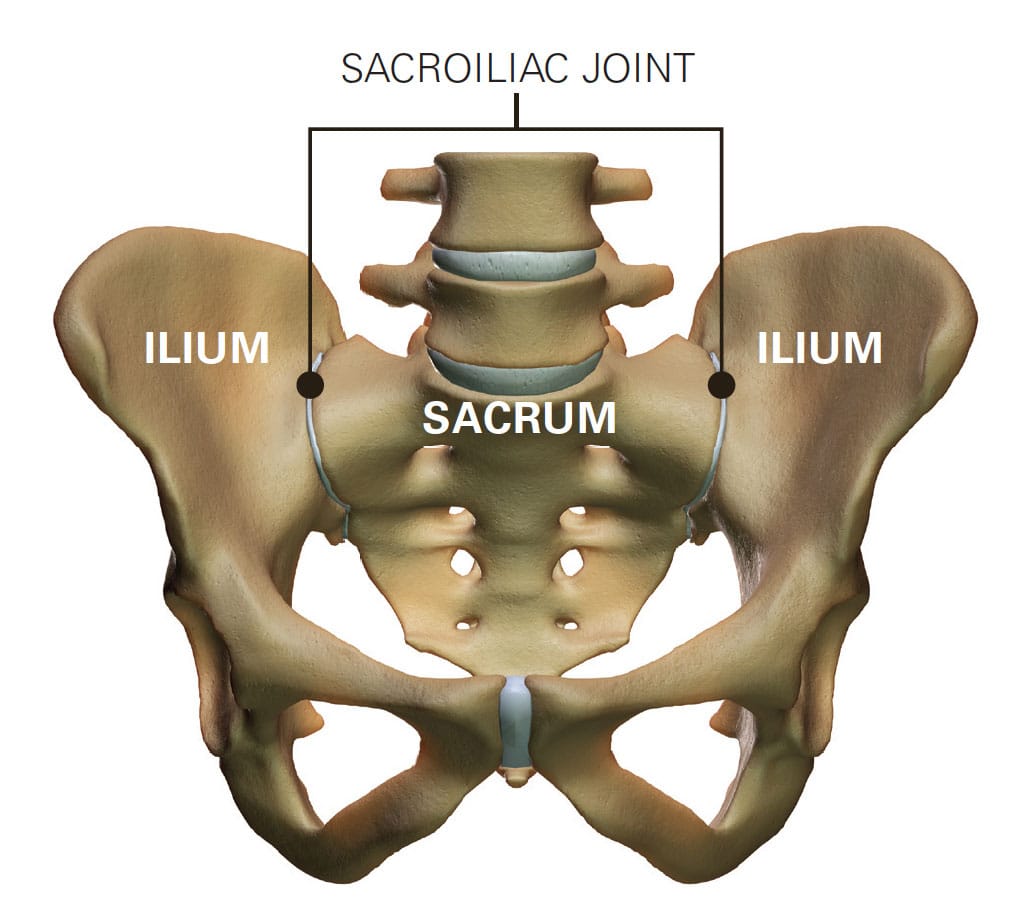
Sacroiliac what? What the difference is between Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction and Sacroiliitis and why it matters!
Aren't sacroiliac joint pain, sacroiliac dysfunction and sacroiliitis all the same thing? Nope! Here we unpick the language and explain why they're different in terms of symptoms, underlying pathology and management in the first post in this series

These tiny joints with hardly any motion play a really important role in walking. Yet, despite their lack of movement, can cause some significant problems in terms of pain and inflammation. So much so that several articles state that anywhere between 15 and 20% of low back pain is actually sacroiliac joint pain!
The terms sacroiliac joint pain and sacroiliac dysfunction are interchangeable, but sacroiliitis isn't and is a completely separate condition. Seen it also used interchangeably? Yup. There is a LOT of this and hopefully, this article will shed light on both conditions and why they are different so you can use the correct term at the correct time!
Revision Time!

We can't really jump into the nuances of this topic without some revision on what the Sacroiliac joints are and why they matter.
The sacroiliac (SI) joints are critical components in our bodies, connecting the iliac bones of the pelvis to the sacrum. These joints are designed to support the weight of the upper body in standing and sitting, and to distribute this weight across the hips and into the lower limbs.
They are synovial joints, meaning they are enveloped in a capsule that contains synovial fluid. This allows for slight, controlled movements that absorb shock and reduce stress on the spine, but for all intents and purposes they move VERY little (no putting your pelvis out of alignment without major trauma sorry - anatomically not possible).
The unique shape and alignment of the joints, along with strong surrounding ligaments, provide stability and limit excessive motion, which is essential for activities like walking, where balance and force transfer are crucial.
SI Joint Pain
Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction, commonly referred to as SI Joint Pain, occurs when the SI joints become irritated or inflamed. This can result from a variety of factors, including injury, pregnancy, arthritis, or even repetitive stress. Symptoms often include:
- Lower back pain
- Pain in the buttocks, hips, or thighs
- Stiffness or a burning sensation in the pelvis
- Discomfort while sitting for long periods
Diagnosis is from a physical examination and patient history. Sometimes an x-ray or MRI may be useful if symptoms are ongoing and vague, however this isn't usually the case.
Treatment is usually physio in the form of exercise based management and managing the pain with pain relief. As you can see from those treatment options it will be managed very well in primary care with a possible referral into secondary care for ongoing physiotherapy. Corticosteroid injections have also been shown to be an effective option if the pain doesn't settle.
Do get subscribed as we are going to discuss the treatment and management options in more detail including evidence in a future article!
Sacroiliitis
Sacroiliitis is a specific term that refers to inflammation of one or both of the sacroiliac joints. Unlike general SI Joint Dysfunction, sacroiliitis is often associated with inflammatory conditions such as ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, or other types of spondyloarthropathies. Key symptoms include:
- Pain and stiffness in the lower back and buttocks
- Pain that worsens with prolonged standing or stair climbing
- Reduced range of motion in the hips
- Other symptoms and signs of inflammatory disease - see SCREEND'EM below
Diagnosing sacroiliitis is like suspecting any inflammatory condition in primary care, take a thorough history and use an appopriate tool such as SCREEND'EM to identify any potential inflammatory red flags and then look to get bloods done to check the patient's inflammatory markers. If strongly suspecting sacroiliitis then refer to rheumatology for further management and advice.
Should you do bloods first? Not always... if this is very acute and onset is less than 3 months consider a direct referral to rheumatology citing early inflammatory arthritis. However, in this patient population we tend to find these symptoms have been going on for a while as it's achey and generalised so generally doing bloods to back up your referral isn't a bad shout.
Treatment focuses on managing inflammation and may include anti-inflammatory medications, physio, and disease-specific treatments if associated with a broader inflammatory condition such as DMARDs.

So let's get to the key bits and takeaways:
What to Look For and Key Differences
While both conditions affect the sacroiliac joints and can cause similar symptoms, there are key differences:
-
Cause: SI Joint Dysfunction is often mechanical (injury, stress, pregnancy), while sacroiliitis is inflammatory
-
Symptoms: Both can cause lower back and pelvic pain, but sacroiliitis may also present with systemic symptoms like a broader pattern of stiffness, no real relief with activity and other generalised joint pains
-
Investigations: in sacroiliitis inflammatory markers will be raised and this is a big clue as to what is going on. These will be essential normal in SI joint dysfunction. X-ray isn't very specific as both can show degeneration of the SI joints
Wrap Up and Conclusions

Understanding the distinction between Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction and Sacroiliitis is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment. While they share commonalities in symptoms and affect the same anatomical structures, their underlying causes and specific management strategies differ significantly.
Correctly identifying and treating these conditions can lead to better patient outcomes, reducing pain and improving quality of life and we can be directly involved in this and have a huge impact from Primary care!
By using the right terminology and understanding these differences, we can better address the challenges posed by sacroiliac joint issues